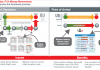
IBM today announced a number of initiatives spanning technology and business consulting that significantly expand its blockchain technology services and solutions. These offerings include a blockchain-as-a-service for developers, IBM “Garages” for blockchain app design and implementation in global financial hubs, blockchain-based IoT via the Watson platform, and an open blockchain technologies project with the London Stock Exchange Group.
The highest profile of these IBM blockchain initiatives is developing open blockchain technologies with the London Stock Exchange Group. The LSE Group’s head of technology innovation, Moiz Kohari, notes that the group is directly engaged with IBM in developing distributed ledger tech that will improve risk management and bring additional transparency. Kohari adds:
“We believe this technology has the potential to drive change across the industry but will need to be developed in partnership with customers and industry participants under an open source approach.”
As a part of its major move into blockchain for enterprise services, IBM has made nearly 44,000 lines of code available to the Linux Foundation’s open source Hyperledger Project to facilitate developers building of secure distributed ledgers.
IBM Global Business Services plans to open “Garages” in London, New York, Singapore and Tokyo to enable IBM consultants to collaborate with developers on the design and implementation of blockchain for business. IBM Global Business Services will also expand its blockchain consulting practice for clients in banking and financial services and logistics. IBM Interactive Experience (IBM iX), Big Blue’s global digital agency, will also engage clients to co-design new use cases for blockchain in more than 25 IBM Studios around the globe.
There are also new blockchain services on the IBM Cloud. Using blockchain services available on Bluemix, developers can access DevOps tools for creating, deploying, running and monitoring blockchain applications on the IBM Cloud. Blockchain applications can also be deployed on IBM z Systems for additional level of security, availability and performance for handling sensitive and regulated data. Blockchain applications can access existing transactions on distributed servers and z Systems through APIs to support new payment, settlement, supply chain and business processes.
Through its Watson IoT Platform, IBM will make it possible for information from devices such as RFID-based locations, barcode-scan events, or device-reported data to be used with IBM’s Blockchain. Devices will be able to communicate to blockchain-based ledgers to update or validate smart contracts. Theoretically, as an IoT-connected package moves along multiple distribution points, the package location and temperature information could be updated on a blockchain. This allows all parties to share information and status of the package as it moves among multiple parties to ensure the terms of a contract are met.
For blockchain-enable IoT for logistics, IBM has also formed a partnership with Finnish technology company, Kouvola Innovation. Mika Lammi, Kouvola’s head of IoT business development, Finland, describes the initiative:
“We’re excited about the potential for blockchain to transform logistics value chains into a more seamless process that provides a trusted view of every piece of cargo. The IBM Blockchain fabric, together with the Watson IoT platform, offers great potential to bring together the physical and digital worlds in a way that has never been done before”
The code that IBM gifted to the Hyperledger project was, according to IBM, developed through the collaboration of more than 35 global IBM Researchers and software developers dedicated to the Linux Foundation project, and more than 100 technical architects focused on making blockchain ready for business.
IBM says it has developed some blockchain-oriented solutions that include a new consensus algorithm developed by IBM Research tailored to specific blockchain use case, advanced identity management built with the latest cryptography, smart contracts that can be written in popular programming languages such as Java or Golang, and privacy and confidentiality control permitting authors of smart contracts to precisely specify permissions.